understanding nutrition labels
The Nutrition Facts panel has two parts:
|
|
||

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
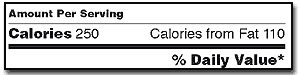
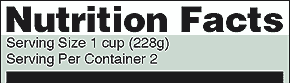
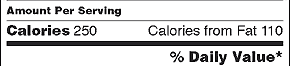
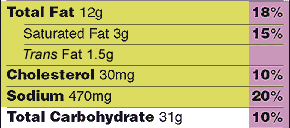
Pay attention to the serving size, including how many servings there are in the food package, and compare it to how much YOU actually eat . The size of the serving on the food package influences all the nutrient amounts listed on the top part of the label. In the sample label above, one serving of macaroni and cheese equals one cup. If you ate the whole package, you would eat two cups. That doubles the calories and other nutrient numbers, including the %Daily Values as shown below (see Calories and %Daily Value for more information).
| Example | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Serving | %DV | Double Serving | %DV | ||
| Serving Size | 1 cup (228g) | 2 cups (456g) | |||
| Calories | 250 | 500 | |||
| Calories from Fat | 110 | 220 | |||
| Total Fat | 12g | 18% | 24g | 36% | |
| Trans Fat | 1.5g | 3g | |||
| Saturated Fat | 3g | 15% | 6g | 30% | |
| Cholesterol | 30mg | 10% | 60mg | 20% | |
| Sodium | 470mg | 20% | 940mg | 40% | |
| Total Carbohydrate | 31g | 10% | 62g | 20% | |
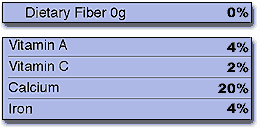
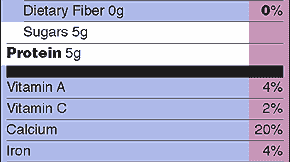
| Dietary Fiber | 0g | 0% | 0g | 0% | |
| Sugars | 5g | 10g | |||
| Protein | 5g | 10g | |||
| Vitamin A | 4% | 8% | |||
| Vitamin C | 2% | 4% | |||
| Calcium | 20% | 40% | |||
| Iron | 4% | 8% | |||
The Nutrients
(#3 and 4 on sample
label):
Look at the top section in the sample nutrition label. It shows
nutrients that are important for your health and separates them into two main
groups:
Remember: You can not only use the food label to help limit those nutrients you want to cut back on, but also to increase those nutrients you want to consume in greater amounts.
The Percent Daily Value (%DV):
![]()
This part of the Nutrition Facts panel tells you whether the nutrients (fat, sodium, fiber, etc) in a serving of food contribute a lot or a little to your total daily diet. By diet we mean all the different foods you eat in a day.
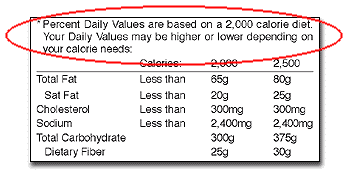 %DVs are based on recommendations for a 2,000
calorie diet.
For labeling purposes, FDA set 2,000 calories as the reference
amount for calculating %DVs. The %DV shows you the percent (or how much) of the
recommended daily amount of a nutrient is in a serving of food. By using the
%DV, you can tell if this amount is high or low. You, like most people, may not
know how many calories you consume in a day. But you can still use the %DV as a
frame of reference, whether or not you eat more or less than 2,000 calories each
day.
%DVs are based on recommendations for a 2,000
calorie diet.
For labeling purposes, FDA set 2,000 calories as the reference
amount for calculating %DVs. The %DV shows you the percent (or how much) of the
recommended daily amount of a nutrient is in a serving of food. By using the
%DV, you can tell if this amount is high or low. You, like most people, may not
know how many calories you consume in a day. But you can still use the %DV as a
frame of reference, whether or not you eat more or less than 2,000 calories each
day.
It's not hard to follow nutrition experts' advice for a healthy diet. Try to limit your total daily intake of fat, saturated fat, sodium, and cholesterol (shown in yellow on the chart) to less than 100%DV.
Likewise, you should try to get enough essential nutrients like calcium, iron, and vitamins A and C as well as other components such as dietary fiber (shown in blue on the chart). Try to average 100% for each one of these nutrients each day.
%DVs are easy to use.
Do you need to know how
to calculate percentages to follow this advice? No, the label (the %DV) does the
math for you. It helps you interpret the numbers (grams and milligrams) by
putting them all on the same scale (0-100%DV), much like a ruler. This way you
can tell high from low and know which nutrients contribute a lot, or a little,
to your daily recommended allowance (upper or lower).
Example of %DV for Total Fat: If you cover up the %DVs on the sample label, can you tell if 12g of Total Fat is high or low? Another way of asking this question is, does one serving (containing 12g of fat) contribute a lot or a little Total Fat to your daily diet?
Now look at the %DVs on the label example: 12g fat equals 18%DV. When one serving of macaroni and cheese contains 18%DV for Total Fat, that means you have 82% of your fat allowance left for all the other foods you eat that day (100%-18%=82%).

Quick Guide to %DV
![]() (#5 on sample label):
(#5 on sample label):
This
general guide tells you that 5%DV or less is low and 20%DV or more is high.
This means that 5%DV or less is low for all nutrients, those you want to
limit (e.g., fat, saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium), and those that you
want to consume in greater amounts (fiber, calcium, etc). As the Quick
Guide shows, 20%DV or more is high for all nutrients.
Example: Look again at the amount of Total Fat in one serving listed on the sample nutrition label for macaroni and cheese. Is 18%DV contributing a lot or a little to your maximum fat limit of 100% DV? Check the Quick Guide to %DV . You see that 18%DV, which is below 20%DV, is not yet high, but what if you ate the whole package (two servings)? You would double that amount, eating 36% of your daily allowance for Total Fat. That amount, coming from just one food, would contribute a lot of fat to your daily diet. It would leave you 64% of your fat allowance (100%-36%=64%) for all of the other foods you eat that day, snacks and drinks included.

Comparisons: The %DV also makes it easy for you to make comparisons. You can compare one product or brand to a similar product. It's easy to see which one is higher or lower in a nutrient because the serving sizes are generally consistent for similar types of foods. See comparison example #1 .
Nutrient Content Claims: You can quickly distinguish one claim from another, such as "reduced fat" vs. "light" or "nonfat." Just compare the %DVs for Total Fat in each food product to see which one is higher or lower in that nutrient-- there is no need to memorize definitions. This works when comparing all nutrient content claims, e.g., less, light, low, free, more, high, etc. See comparison example #1 and #2
Dietary Trade-Offs: You can use the %DV to help you make dietary trade-offs with other foods throughout the day. You don't have to give up a favorite food to eat a healthy diet. When a food you like is high in fat, balance it with foods that are low in fat at other times of the day. Also, pay attention to how much you eat so that the total amount of fat for the day stays below 100%DV.
Nutrients that Have No %DV: Trans Fats, Sugars, and
Protein:
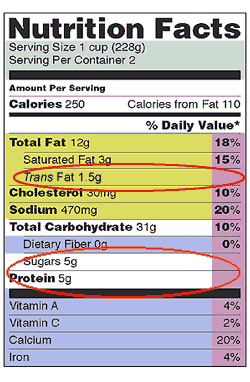 Note that Trans fat, Sugars and, Protein
do not list a %DV on the Nutrition Facts panel.
Note that Trans fat, Sugars and, Protein
do not list a %DV on the Nutrition Facts panel.
Trans Fat: Scientific reports link trans fat (and saturated fat) with raising LDL ("bad") blood cholesterol levels, both of which increase your risk of coronary heart disease, a leading cause of death in the US. But experts could not provide a reference value for trans fat nor any other information that FDA believes is sufficient to establish a Daily Value or %DV.
Sugars: No daily reference value has been established because no recommendations have been made for the total amount of sugars to eat in a day. Keep in mind, the sugars listed on the Nutrition Facts panel include naturally occurring sugars (like those in fruit and milk) as well as those added to a food or drink. Check the ingredient list for specifics on added sugars.
Protein: A %DV is required to be listed if a claim is made for protein, such as "high in protein". Otherwise, unless the food is meant for use by infants and children under 4 years old, none is needed. Current scientific evidence indicates that protein intake is not a public health concern for adults and children over 4 years of age.
To limit nutrients that have no %DV, like trans fat and sugars, compare the labels of similar products and choose the food with the lowest amount.
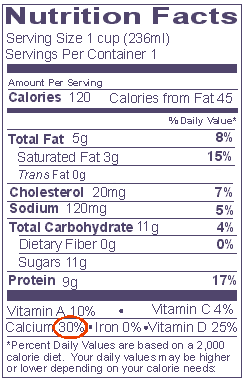
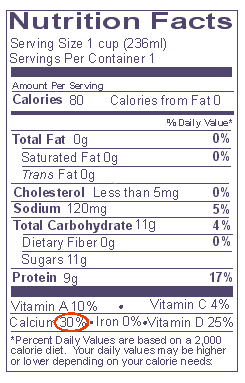
Calcium: Experts advise consumers to consume adequate amounts of calcium in their daily diet. This advice is given in milligrams (mg), but the Nutrition Facts panel only lists a %DV for calcium. For consumers to know how the calcium they consume relates to expert advice, they need to do some simple math. (This applies to calcium only).
Example: Experts advise adolescents, especially girls, to consume 1,300mg and post-menopausal women 1,200mg of calcium daily. To find the %DV that corresponds with 1,300mg and 1,200mg, just divide the number of mg by 10. (The DV for calcium on food labels is 1,000mg). When converted to a percent, this gives a factor of 10. Thus, the daily target for teenage girls, 1,300mg , equals 130%DV, and the daily target for post menopausal women, 1,200mg, equals 120%DV.
If you want to convert the %DV for calcium into milligrams, just multiply by 10. A container of yogurt might list 30%DV for calcium. To convert this to milligrams, multiply by 10, which equals 300mg of calcium for the yogurt.

Equivalencies 30% DV = 300mg calcium = one cup of milk 100% DV = 1,000mg calcium 130% DV = 1,300mg calcium
The important thing is to look at the %DV for calcium on the food package so you know how much one serving contributes to the total amount you need. Remember, a food with 20%DV or more contributes a lot of calcium to your daily total, while one with 5%DV or less contributes a little. See Comparison Example #2 .
The Footnote, or lower part
of the
Nutrition Facts Panel
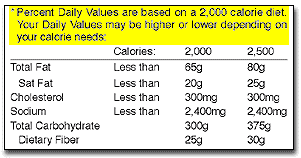 (#6 on sample label)
(#6 on sample label)
Note the *
used after the heading "%Daily Value" on the Nutrition Facts panel. It refers to
the Footnote in the lower part of the nutrition label, which tells you that
"%DVs are based on recommendations for a 2,000 calorie diet". This
statement must be on all food labels. But the remaining information in the full
footnote may not be on the package if the size of the label is too small. When
the full footnote does appear, it will always be the same. It doesn't change
from product to product, because it shows dietary advice for all Americans--it
is not about a specific food product.
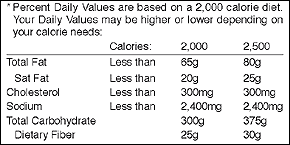
The Daily Values are based on expert dietary advice about how much, or how little, of some key nutrients you should eat each day, depending on whether you eat 2,000 or 2,500 calories a day.
Example: look at the Total Fat information in the footnote. It tells you that if you eat a 2,000 calorie diet, you should eat less than 65g of fat in all the foods you eat in a day. By doing this, you will follow nutrition experts' advice to consume no more than 30 percent of your daily calories from fat. Because the DV for total fat is "less than 65g," this is the same thing as saying, to keep your total fat intake for the day below 100%DV.
If you consume 2,500 calories per day, the Footnote shows you how your daily values would change for some nutrients but not for others. The Daily Values for Cholesterol (300mg) and Sodium (2,400mg sodium) remain the same no matter how many calories you eat. But recommended levels of intake for other nutrients do depend on how many calories you consume.
Remember: %DVs listed on the top half of the food label are based on recommendations for a 2,000 calorie diet, not a 2,500 calorie diet.
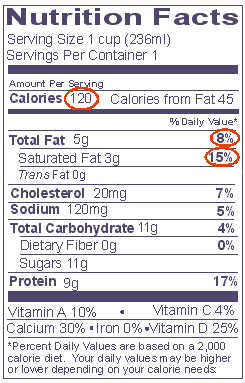
Comparison Example #1
|
Below are two kinds of milk- one is "Reduced Fat," the other
is chocolate "Nonfat" milk. Each serving size is one cup. Which has more
calories? Which is higher in fat and saturated fat? |
|
|
REDUCED FAT MILK 2% Milkfat |
CHOCOLATE NONFAT MILK
|
|---|---|
|

|
Comparison Example #2
|
Below are two kinds of milk- one is "Reduced Fat," the other
is chocolate "Nonfat" milk. Each serving size is one cup. Which has more
calcium? |
|
|
REDUCED FAT MILK 2% Milkfat |
CHOCOLATE NONFAT MILK
|
|---|---|
|
|